
In contrast, if ON and OFF are UNIX applications, ON can send to OFF, but OFF cannot send to ON.įrom what I have read this is setting may be disabled by default on Windows and enabled by default on Linux, but I haven't tested it myself.Īs an important side note, the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option is entirely different from the IPV6_MULTICAST_LOOP option, referring to the Linux ip(7) and ipv6(7) man pages: If ON and OFF are Winsock applications, OFF can send to ON, but ON cannot sent to OFF. In the UNIX version, the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option applies to the send path.įor example, applications ON and OFF (which are easier to than X and Y) join the same group on the same interface application ON sets the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option on, application OFF sets the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option off.In Winsock, the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option applies only to the receive path.The Winsock version of the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option is semantically different than the UNIX version of the IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option: IP_MULTICAST_LOOP-Controls loopback of multicast traffic.This is configured by the standard IP_MULTICAST_LOOP option, which is best summarized by the IP Multicast MSDN article (archived):Ĭurrently, most IP multicast implementations use a set of socket options proposed by Steve Deering to the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). This means that the operating system is responsible for forwarding traffic to other programs or sockets on the same host that joined a multicast group, since it won't be read from the interface. On the hardware level, multicast traffic is treated like broadcast traffic in that it is not routed back to the physical port it was sent from in order to prevent link level loops. It is difficult to search for this problem specifically with regards to operating system behavior or standardization. This is quite a common question with many StackOverflow questions on it, but they are often misunderstood or poorly worded. The real problem is having programs on the same host receive multicast data sent by each other (or, equivalently, having sockets within a single program receive multicast data sent by each other), when they're both configured to use the same multicast group. However, this is typically only necessary if there are other computers on the network that may interfere by using the same multicast group. Transmit_file(argv,argv,INTERFACE_IP,UDP_PORT) īinding or routing to the loopback device is necessary if you do not want IP multicast traffic (such as IGMP messages) to be sent across the network. I have already tried following commands sudo ifconfig lo multicastĪny suggestion in this regard would be very helpful. I'm able to see packet getting transmitted in wireshark but the src ip is taken from my default network interface (i.e interface which is my default gateway) But when tried to play the same on vlc it didn't worked. Leaving aside other bitrate and controlled multicast issues, I tried to read one video file and multicast on loopback device. The idea is to receive a video stream via RTSP/HTTP or any other network protocol and multicast it on the loopback address so that I can use VLC to play the stream using multicast address. The Wikipedia Page has good information on it.I wish to send UDP multicast packets to loopback address and receive the same in other application. I don't know if I explained it very well, but it was the best I could do.
WHAT IS THE LOOPBACK ADDRESS SOFTWARE
This would provide the information to local applications, while disabling the ability for somebody else on a LAN to access whatever server software you set up as local. You can specify the server software to transfer information via the loopback address and your client software could listen in on the loop back address. This can be seen when you have a server-client model application installed on the local computer, but you do not want that information to be accessible remotely. It can also be used to specify to your applications that you do not want your information to leave the host computer.

If you suspect that your NIC is not working on a physical level, this makes a very good test. When you do this you are testing to make sure that your information can go down to layer 1 and back up.
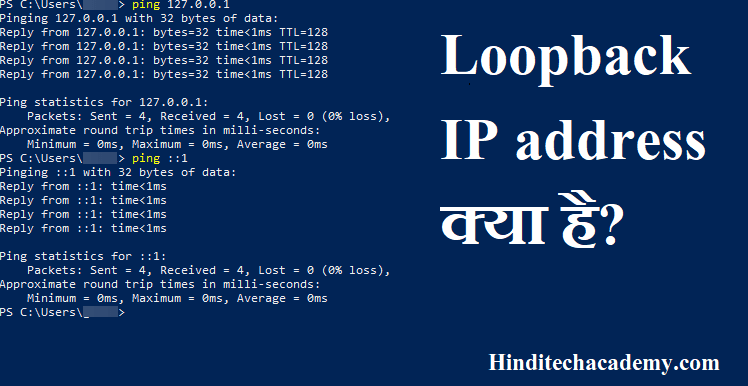
When you test your NIC, this can be done via "ping 127.0.0.1".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
